- Fener Mah. Bulent Ecevit Blv. No:72 Muratpasa/ANTALYA
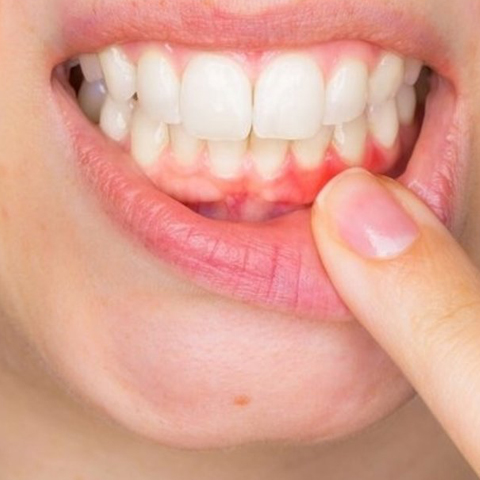
It is the inflammation of the gingival connective tissue caused by bacteria entering the tissue from the separations in the gum structure due to any reason For example, during brush trauma, chewing of hard foods, tissue integrity may deteriorate and highly virulent microorganisms can be pushed into the gums. It is a lesion that only concerns the gum, usually the size of a pinhead, slightly painful and slightly higher than the surface.
Initially red colored then yellowish color. When it is drained, the pain disappears and heals easily, in the early period a prulent fluid accumulates in the form of a bright, smooth surface, red-colored swelling in 1-2 days and becomes fluke, mostly drains spontaneously, the area is filled with granulation tissue and recovery occurs. The patient is recommended to gargle with warm salt water.
A healthy gum should be an orange peel (light pink) color. There are no complaints such as bleeding, inflammation, swelling, redness in healthy gums, but individuals with abscesses in the gums for any reason have complaints such as inflammation, swelling, and pain in the gums. In more advanced abscesses, it may cause minor bleeding in the gums and odor in the mouth.
Individuals with abscesses in the gums usually complain of pain in the teeth close to the abscess.
Sometimes the abscess may burst due to the growth in the volume of the abscess and the exudate inside may come out. If individuals encounter such symptoms, they should consult a dentist, the factor causing this situation is eliminated and the necessary treatment is applied.
Systemic antibiotics are recommended to be used only in certain conditions and patients in the treatment of periodontal diseases. If individuals with periodontal disease feel pain due to this reason and the problem will disappear with antibiotic treatment, antibiotic treatment should be applied, but in cases where antibiotic use is contraindicated, the person should avoid using antibiotics. In some patients, antibiotics applied alone without mechanical treatment remain ineffective due to the presence of pathogenic microorganisms in a well-organized biofilm layer.
Antibiotics can be used at the stage when periodontal treatment is completed and the maintenance phase is completed before starting mechanical therapy, with or without mechanical treatment.
Copyright © 2025 Orion. Tüm Hakları Saklıdır.